415. 大数相加
腾讯 WXG 一面
✅ LeetCode: 415. 字符串相加
给定两个字符串形式的非负整数 num1 和 num2 ,计算它们的和并同样以字符串形式返回。
你不能使用任何內建的用于处理大整数的库(比如 BigInteger), 也不能直接将输入的字符串转换为整数形式。
示例 1:
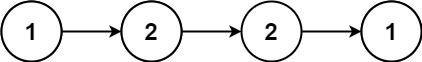
1 2 输入:num1 = "11", num2 = "123" 输出:"134"
示例 2:
1 2 输入:num1 = "456", num2 = "77" 输出:"533"
1️⃣ 解法一:对位数较短的数字进行了补零操作(预处理):self-AC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution {public : string addStrings (string num1, string num2) { int m = num1.l ength(), n = num2.l ength(); int len = abs (m - n); string zero (len, '0' ) ; if (m < n) num1 = zero + num1; else if (m > n) num2 = zero + num2; int mx = max (m, n); int remain = 0 ; string ans; for (int i = mx - 1 ; i >= 0 || remain; i--) { if (i < 0 && remain) { ans.push_back ('1' ); break ; } char ch = num1[i] + (num2[i] - '0' ) + remain; if (ch > '9' ) { ch = ch - 10 ; remain = 1 ; } else { remain = 0 ; } ans.push_back (ch); } reverse (ans.begin (), ans.end ()); return ans; } };
2️⃣ 解法二:去除预处理的过程,直接模拟
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public : string addStrings (string num1, string num2) { int i = num1.l ength() - 1 , j = num2.l ength() - 1 , add = 0 ; string ans = "" ; while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add) { int x = i >= 0 ? num1[i] - '0' : 0 ; int y = j >= 0 ? num2[j] - '0' : 0 ; int result = x + y + add; ans.push_back ('0' + result % 10 ); add = result / 10 ; i--; j--; } reverse (ans.begin (), ans.end ()); return ans; } };
43. 大数相乘
小鹏汽车智驾一面
✅ LeetCode: 43. 字符串相乘
给定两个以字符串形式表示的非负整数 num1 和 num2,返回 num1 和 num2 的乘积,它们的乘积也表示为字符串形式。
**注意:**不能使用任何内置的 BigInteger 库或直接将输入转换为整数。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: num1 = "2", num2 = "3" 输出: "6"
示例 2:
1 2 输入: num1 = "123", num2 = "456" 输出: "56088"
1️⃣ 解法一思路(竖式相加):建立在「大数相加」的基础上,因为多个数之间需要累加(这段代码自己 AC 的,容易理解)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 class Solution {public : string addStrings (string num1, string num2) { int i = num1.l ength() - 1 , j = num2.l ength() - 1 , add = 0 ; string ans = "" ; while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add) { int x = i >= 0 ? num1[i] - '0' : 0 ; int y = j >= 0 ? num2[j] - '0' : 0 ; int result = x + y + add; add = result / 10 ; ans.push_back ('0' + result % 10 ); i--; j--; } reverse (ans.begin (), ans.end ()); return ans; } string multiply (string num1, string num2) { if (num1 == "0" || num2 == "0" ) return "0" ; int multiply = 0 ; int m = num1.l ength(), n = num2.l ength(); string ans = "0" ; for (int i = m - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int x = num1[i] - '0' ; string num; int add = 0 ; for (int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 || add; j--) { if (x == 0 ) { num = "0" ; break ; } if (j < 0 ) { num.push_back ('0' + add); break ; } int y = num2[j] - '0' ; int result = x * y + add; add = result / 10 ; num.push_back ('0' + result % 10 ); } reverse (num.begin (), num.end ()); if (num != "0" ) ans = addStrings (ans, num + string (multiply, '0' )); multiply++; } return ans; } };
2️⃣ 解法二:直接做乘法,长度分别为 m 和 n 的数字相乘,值长度不超过 m + n,vector<int> ansArr(m + n)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution {public : string multiply (string num1, string num2) { if (num1 == "0" || num2 == "0" ) { return "0" ; } int m = num1.l ength(), n = num2.l ength(); vector<int > ansArr (m + n) ; for (int i = m - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int x = num1[i] - '0' ; for (int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { int y = num2[j] - '0' ; ansArr[i + j + 1 ] += x * y; } } for (int i = m + n - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { ansArr[i - 1 ] += ansArr[i] / 10 ; ansArr[i] %= 10 ; } int idx = ansArr[0 ] == 0 ? 1 : 0 ; string ans; while (idx < m + n) { ans.push_back ('0' + ansArr[idx]); idx++; } return ans; } };
239. 滑动窗口最大值
腾讯 WXG 一面
✅ LeetCode: 239. 滑动窗口最大值
给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 输入:nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3 输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7] 解释: 滑动窗口的位置 最大值 --------------- ----- [1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
1️⃣ 优先队列 priority_queue(记录最大值) + 哈希表(记录删除元素):self-AC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public : vector<int > maxSlidingWindow (vector<int >& nums, int k) { priority_queue<int , vector<int >, less<int >> pq; int n = nums.size (); unordered_map<int , int > cnt; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) pq.push (nums[i]); vector<int > ans{pq.top ()}; for (int i = k; i < n; i++) { cnt[nums[i - k]]++; pq.push (nums[i]); while (pq.size () > k && cnt[pq.top ()] > 0 ) { cnt[pq.top ()]--; pq.pop (); } ans.push_back (pq.top ()); } return ans; } };
2️⃣ 优先队列 priority_queue<pair<int, int>>,通过记录索引值判断 pq.top() 元素是否在定长窗口内
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public : vector<int > maxSlidingWindow (vector<int >& nums, int k) { priority_queue<pair<int , int >> pq; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { pq.emplace (nums[i], i); } vector<int > ans{pq.top ().first}; for (int i = k; i < nums.size (); i++) { pq.emplace (nums[i], i); while (pq.top ().second < i - k + 1 ) { pq.pop (); } ans.push_back (pq.top ().first); } return ans; } };
206. 反转链表
腾讯 WXG 一面
✅ LeetCode: 206. 反转链表
相关例题 —— 92. 反转链表 II :反转部分区间,找到区间 leftNode 与 rightNode,以及 leftNode 左节点 pre 与 rightNode 右节点 nxt,独立区间(断开连接)后反转再接回。
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
1️⃣ 解法一:递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 struct ListNode { int val; ListNode* next; ListNode () : val (0 ), next (nullptr ) {} ListNode (int x) : val (x), next (nullptr ) {} ListNode (int x, ListNode* next) : val (x), next (next) {}; }; class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { if (!head || !head->next) { return head; } ListNode* new_head = reverseList (head->next); head->next->next = head; head->next = nullptr ; return new_head; } };
2️⃣ 解法二:三指针迭代(pre = nullptr, cur = head, nxt = cur->next)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { ListNode* pre = nullptr ; ListNode* cur = head; while (cur) { ListNode* nxt = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = nxt; } return pre; } };
146. LRU 缓存
腾讯 WXG 一面|腾讯 CSIG 一面|腾讯 PCG 一面
据说是所有面试中出现概率的 No.1
✅ LeetCode: 146. LRU 缓存 、面试题 16.25. LRU 缓存
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity) 以 正整数 作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字 key 已经存在,则变更其数据值 value ;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组 key-value 。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过 capacity ,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 输入 ["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]] 输出 [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4] 解释 LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2); lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1} lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1 lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3} lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3 lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
LRUCache:循环双向链表 + 哈希表
循环:方便获取末尾节点进行 LRU 逐出/删除
双向链表
哈希表:快速找到 key 对应的节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 class Node {public : int key; int value; Node* prev; Node* next; Node (int k = 0 , int v = 0 ) : key (k), value (v) {} }; class LRUCache {private : int capacity; Node* dummy; unordered_map<int , Node*> key_to_node; void remove (Node* x) x->prev->next = x->next; x->next->prev = x->prev; } void push_front (Node* x) x->prev = dummy; x->next = dummy->next; x->prev->next = x; x->next->prev = x; } Node* get_node (int key) { auto it = key_to_node.find (key); if (it == key_to_node.end ()) { return nullptr ; } Node* node = it->second; remove (node); push_front (node); return node; } public : LRUCache (int capacity) : capacity (capacity), dummy (new Node ()) { dummy->prev = dummy; dummy->next = dummy; } int get (int key) Node* node = get_node (key); return node ? node->value : -1 ; } void put (int key, int value) Node* node = get_node (key); if (node) { node->value = value; return ; } node = new Node (key, value); key_to_node[key] = node; push_front (node); if (key_to_node.size () > capacity) { Node* back_node = dummy->prev; key_to_node.erase (back_node->key); remove (back_node); delete back_node; } } };
460. LFU 缓存
华为机考
✅ LeetCode: 460. LFU 缓存
相关例题:146. LRU 缓存
请你为 最不经常使用(LFU) 缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。
实现 LFUCache 类:
LFUCache(int capacity) - 用数据结构的容量 capacity 初始化对象int get(int key) - 如果键 key 存在于缓存中,则获取键的值,否则返回 -1 。void put(int key, int value) - 如果键 key 已存在,则变更其值;如果键不存在,请插入键值对。当缓存达到其容量 capacity 时,则应该在插入新项之前,移除最不经常使用的项。在此问题中,当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,应该去除 最久未使用 的键。
为了确定最不常使用的键,可以为缓存中的每个键维护一个 使用计数器 。使用计数最小的键是最久未使用的键。
当一个键首次插入到缓存中时,它的使用计数器被设置为 1 (由于 put 操作)。对缓存中的键执行 get 或 put 操作,使用计数器的值将会递增。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 输入: ["LFUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [3], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]] 输出: [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, 3, null, -1, 3, 4] 解释: // cnt(x) = 键 x 的使用计数 // cache=[] 将显示最后一次使用的顺序(最左边的元素是最近的) LFUCache lfu = new LFUCache(2); lfu.put(1, 1); // cache=[1,_], cnt(1)=1 lfu.put(2, 2); // cache=[2,1], cnt(2)=1, cnt(1)=1 lfu.get(1); // 返回 1 // cache=[1,2], cnt(2)=1, cnt(1)=2 lfu.put(3, 3); // 去除键 2 ,因为 cnt(2)=1 ,使用计数最小 // cache=[3,1], cnt(3)=1, cnt(1)=2 lfu.get(2); // 返回 -1(未找到) lfu.get(3); // 返回 3 // cache=[3,1], cnt(3)=2, cnt(1)=2 lfu.put(4, 4); // 去除键 1 ,1 和 3 的 cnt 相同,但 1 最久未使用 // cache=[4,3], cnt(4)=1, cnt(3)=2 lfu.get(1); // 返回 -1(未找到) lfu.get(3); // 返回 3 // cache=[3,4], cnt(4)=1, cnt(3)=3 lfu.get(4); // 返回 4 // cache=[3,4], cnt(4)=2, cnt(3)=3
LFU 缓存 = 循环双向链表 + key_to_node 哈希表 + freq_to_dummy 哈希表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 class Node {public : int key; int value; int freq = 1 ; Node* prev; Node* next; Node (int k = 0 , int v = 0 ) : key (k), value (v) {} }; class LFUCache {private : int min_freq; int capacity; unordered_map<int , Node*> key_to_node; unordered_map<int , Node*> freq_to_dummy; Node* new_list () { Node* dummy = new Node (); dummy->prev = dummy; dummy->next = dummy; return dummy; } void remove (Node* node) node->prev->next = node->next; node->next->prev = node->prev; } void push_front (int freq, Node* node) auto it = freq_to_dummy.find (freq); if (it == freq_to_dummy.end ()) { it = freq_to_dummy.emplace (freq, new_list ()).first; } Node* dummy = it->second; node->prev = dummy; node->next = dummy->next; node->prev->next = node; node->next->prev = node; } Node* get_node (int key) { auto it = key_to_node.find (key); if (it == key_to_node.end ()) { return nullptr ; } Node* node = it->second; remove (node); Node* dummy = freq_to_dummy[node->freq]; if (dummy->prev == dummy) { freq_to_dummy.erase (node->freq); delete dummy; if (min_freq == node->freq) { min_freq++; } } push_front (++node->freq, node); return node; } public : LFUCache (int capacity) : capacity (capacity) {} int get (int key) Node* node = get_node (key); return node ? node->value : -1 ; } void put (int key, int value) Node* node = get_node (key); if (node) { node->value = value; return ; } if (key_to_node.size () == capacity) { Node* dummy = freq_to_dummy[min_freq]; Node* last_node = dummy->prev; key_to_node.erase (last_node->key); remove (last_node); delete last_node; if (dummy->prev == dummy) { freq_to_dummy.erase (min_freq); delete dummy; } } node = new Node (key, value); key_to_node[key] = node; push_front (1 , node); min_freq = 1 ; } };
560. 和为 k 的子数组
Momenta 一面
✅ LeetCode: 560. 和为 K 的子数组
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你统计并返回该数组中和为 k 的子数组的个数 。
子数组是数组中元素的连续非空序列。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:nums = [1,1,1], k = 2 输出:2
示例 2:
1 2 输入:nums = [1,2,3], k = 3 输出:2
1️⃣ 前缀和 + 哈希表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public : int subarraySum (vector<int >& nums, int k) int n = nums.size (); vector<int > preSum (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) preSum[i] = nums[i - 1 ] + preSum[i - 1 ]; int ans = 0 ; unordered_map<int , int > cnt; for (int num : preSum) { ans += cnt.contains (num - k) ? cnt[num - k] : 0 ; cnt[num]++; } return ans; } };
93. 复原 IP 地址
腾讯 PCG 一面
✅ LeetCode: 93. 复原 IP 地址
有效 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 '.' 分隔。
例如:"0.1.2.201" 和 "192.168.1.1" 是 有效 IP 地址,但是 "0.011.255.245"、"192.168.1.312" 和 "192.168@1.1" 是 无效 IP 地址。
给定一个只包含数字的字符串 s ,用以表示一个 IP 地址,返回所有可能的有效 IP 地址 ,这些地址可以通过在 s 中插入 '.' 来形成。你 不能 重新排序或删除 s 中的任何数字。你可以按 任何 顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:s = "25525511135" 输出:["255.255.11.135","255.255.111.35"]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:s = "0000" 输出:["0.0.0.0"]
1️⃣ 解法一:四层循环迭代,简单易懂暴力
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public : vector<string> restoreIpAddresses (string s) { int n = s.length (); vector<string> ans; for (int a = 1 ; a <= 3 ; a++) { for (int b = 1 ; b <= 3 ; b++) { for (int c = 1 ; c <= 3 ; c++) { for (int d = 1 ; d <= 3 ; d++) { if (a + b + c + d == n) { int numA = stoi (s.substr (0 , a)); int numB = stoi (s.substr (a, b)); int numC = stoi (s.substr (a + b, c)); int numD = stoi (s.substr (a + b + c, d)); if (numA <= 255 && numB <= 255 && numC <= 255 && numD <= 255 ) { string ip = to_string (numA) + "." + to_string (numB) + "." + to_string (numC) + "." + to_string (numD); if (ip.length () == n + 3 ) { ans.push_back (ip); } } } } } } } return ans; } };
2️⃣ 回溯法|递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 class Solution {public : vector<string> ans; string ip; void backtracking (string s, int i, int segment) if (i == s.length () && segment == 4 ) { ip = ip.substr (0 , ip.length () - 1 ); ans.push_back (ip); return ; } if (segment > 4 ) { return ; } for (int j = 1 ; j <= 3 && i + j - 1 < s.length (); j++) { if (j > 1 && s[i] == '0' ) { return ; } string subIP = s.substr (i, j); int numIP = stoi (subIP); if (numIP > 255 ) break ; int len = ip.length (); ip = ip + subIP + '.' ; backtracking (s, i + j, segment + 1 ); ip = ip.substr (0 , len); } } vector<string> restoreIpAddresses (string s) { int n = s.length (); if (n < 4 ) { return {}; } backtracking (s, 0 , 0 ); return ans; } }; class Solution {public : vector<string> ans; vector<string> path; vector<string> restoreIpAddresses (string s) { int n = s.length (); if (n < 4 || n > 12 ) { return {}; } function<void (int )> dfs = [&](int i) { if (i == n && path.size () == 4 ) { string ip = path[0 ] + "." + path[1 ] + "." + path[2 ] + "." + path[3 ]; ans.push_back (ip); return ; } for (int j = 1 ; j <= 3 && i + j - 1 < n; j++) { string sub = s.substr (i, j); if ((j > 1 && s[i] == '0' ) || stoi (sub) > 255 ) break ; path.push_back (sub); dfs (i + j); path.pop_back (); } }; dfs (0 ); return ans; } };
25. K 个一组反转链表
腾讯 WXG 一面
✅ LeetCode: 25. K 个一组翻转链表
相关例题 1:24. 两两交换链表中的节点
相关例题 2:206. 反转链表
相关例题 3:92. 反转链表 II
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
1️⃣ 解法一:利用「206. 反转链表」+「92. 反转链表 II」完成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { ListNode* pre = nullptr ; ListNode* cur = head; while (cur) { ListNode* nxt = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = nxt; } return pre; } ListNode* reverseBetween (ListNode* head, int left, int right) { ListNode dummy (0 , head) ; ListNode* pre = &dummy; for (int i = 0 ; i < left - 1 ; i++) { pre = pre->next; } ListNode* leftNode = pre->next; ListNode* rightNode = leftNode; for (int i = left; i < right; i++) { rightNode = rightNode->next; } ListNode* nxt = rightNode->next; rightNode->next = nullptr ; reverseList (leftNode); pre->next = rightNode; leftNode->next = nxt; return dummy.next; } ListNode* reverseKGroup (ListNode* head, int k) { int n = 0 ; ListNode* cur = head; while (cur) { n++; cur = cur->next; } if (n < k) { return head; } ListNode* new_head = head; int times = n / k; for (int i = 0 ; times--; i += k) { ListNode* node = reverseBetween (new_head, i + 1 , i + k); if (i == 0 ) { new_head = node; } } return new_head; } };
2️⃣ 解法二|0x3f:从反转链表直接到「K 个一组翻转链表」
反转过程同「反转链表」代码,从 while (cur) 变成 for (int i = 0; i < k; i++);其次每处理 k 个一组后,节点之间需要切换(🌟)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseKGroup (ListNode* head, int k) { int n = 0 ; for (ListNode* cur = head; cur; cur = cur->next) { n++; } ListNode dummy (0 , head) ; ListNode* p0 = &dummy; ListNode* pre = nullptr ; ListNode* cur = head; for (; n >= k; n -= k) { for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { ListNode* nxt = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = nxt; } ListNode* nxt = p0->next; p0->next->next = cur; p0->next = pre; p0 = nxt; } return dummy.next; } };
234. 回文链表 ✅ LeetCode: 234. 回文链表
相关例题:
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,2,1] 输出:true
先找到中间节点(类 876 题使用快慢指针),然后反转后半段的链表(206 题反转链表),之后逐个比较即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 class Solution {public : ListNode* middleNode (ListNode* head) { ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head; while (fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } return slow; } ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { ListNode* pre = nullptr ; ListNode* cur = head; while (cur) { ListNode* nxt = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = nxt; } return pre; } ListNode* recursion_reverseList (ListNode* head) { if (!head || !head->next) { return head; } ListNode* new_head = recursion_reverseList (head->next); head->next->next = head; head->next = nullptr ; return new_head; } bool isPalindrome (ListNode* head) ListNode* middle = middleNode (head); ListNode* node = reverseList (middle); while (node) { if (head->val != node->val) { return false ; } head = head->next; node = node->next; } return true ; } };
23. 合并 K 个升序链表
快手搜广推一面
✅ LeetCode: 23. 合并 K 个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:链表数组如下: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
1️⃣ 最小堆
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution {public : ListNode* mergeKLists (vector<ListNode*>& lists) { auto cmp = [](const ListNode* a, const ListNode* b) { return a->val > b->val; }; priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, decltype (cmp)> pq; for (auto head : lists) { if (head) { pq.push (head); } } ListNode dummy{}; auto cur = &dummy; while (!pq.empty ()) { ListNode* nxt = pq.top (); pq.pop (); cur->next = nxt; cur = cur->next; if (nxt->next) { pq.push (nxt->next); } } return dummy.next; } };
2️⃣ 分治法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution {public : ListNode* mergeTwoLists (ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) { ListNode dummy{}; ListNode* cur = &dummy; while (list1 && list2) { if (list1->val < list2->val) { cur->next = list1; list1 = list1->next; } else { cur->next = list2; list2 = list2->next; } cur = cur->next; } cur->next = list1 ? list1 : list2; return dummy.next; } ListNode* mergeKLists (vector<ListNode*>& lists, int l, int r) { if (l == r) return lists[l]; if (l > r) return nullptr ; int m = (l + r) >> 1 ; auto left = mergeKLists (lists, l, m); auto right = mergeKLists (lists, m + 1 , r); return mergeTwoLists (left, right); } ListNode* mergeKLists (vector<ListNode*>& lists) { return mergeKLists (lists, 0 , lists.size () - 1 ); } };
445. 两数相加 II
腾讯 CDG 一面
✅ LeetCode: 445. 两数相加 II
前置题目:
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
示例1:
1 2 输入:l1 = [7,2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,8,0,7]
反转链表 + 两数相加 = 秒杀
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr ) { return head; } auto new_head = reverseList (head->next); head->next->next = head; head->next = nullptr ; return new_head; } ListNode* addTwo (ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2, int carry = 0 ) { if (l1 == nullptr && l2 == nullptr ) { return carry ? new ListNode (carry) : nullptr ; } if (l1 == nullptr ) { swap (l1, l2); } carry += l1->val + (l2 ? l2->val : 0 ); l1->val = carry % 10 ; l1->next = addTwo (l1->next, (l2 ? l2->next : nullptr ), carry / 10 ); return l1; } public : ListNode* addTwoNumbers (ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { l1 = reverseList (l1); l2 = reverseList (l2); auto l3 = addTwo (l1, l2); return reverseList (l3); } };
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
腾讯 CSIG 一面
✅ LeetCode: 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]
四个指针秒了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public : ListNode* swapPairs (ListNode* head) { if (!head) return head; ListNode dummy (0 , head) ; ListNode* node0 = &dummy; ListNode* node1 = head; while (node1 && node1->next) { ListNode* node2 = node1->next; ListNode* node3 = node2->next; node2->next = node1; node1->next = node3; node0->next = node2; node0 = node1; node1 = node3; } return dummy.next; } };
72. 编辑距离
腾讯 CDG 一面
✅ LeetCode: 72. 编辑距离
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2, 请返回将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。
你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 输入:word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros" 输出:3 解释: horse -> rorse (将 'h' 替换为 'r') rorse -> rose (删除 'r') rose -> ros (删除 'e')
递推|注意边界初始化值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public : int minDistance (string word1, string word2) int m = word1.l ength(), n = word2.l ength(); vector<vector<int >> f (m + 1 , vector <int >(n + 1 )); for (int i = 0 ; i <= m; i++) f[i][0 ] = i; for (int j = 0 ; j <= n; j++) f[0 ][j] = j; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { f[i + 1 ][j + 1 ] = word1[i] == word2[j] ? f[i][j] : min ({f[i][j], f[i + 1 ][j], f[i][j + 1 ]}) + 1 ; } } return f[m][n]; } };
4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
字节 AML 一面
✅ LeetCode: 4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
给定两个大小分别为 m 和 n 的正序(从小到大)数组 nums1 和 nums2。请你找出并返回这两个正序数组的 中位数 。
算法的时间复杂度应该为 O(log (m+n)) 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2] 输出:2.00000 解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3] ,中位数 2
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4] 输出:2.50000 解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3,4] ,中位数 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5
🧐 分析 本质上,我们需要在两个有序数组中,查找第 k 小的数,其中 k = (m + n) / 2 取上整 。
如果 m+n 是奇数,返回第 k 小的数。
如果 m+n 是偶数,返回第 k 小的数和第 k+1 小的数的平均值。
先从最暴力的「排序」做法开始,然后讲解「双指针」做法,最后过渡到「二分查找」做法。
🙋 答疑
1️⃣ 相向双指针|均匀分组|当条件「第一组最大值 <= 第二组最小值」满足 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public : double findMedianSortedArrays (vector<int >& a, vector<int >& b) if (a.size () > b.size ()) swap (a, b); int m = a.size (), n = b.size (); a.insert (a.begin (), INT_MIN); b.insert (b.begin (), INT_MIN); a.push_back (INT_MAX); b.push_back (INT_MAX); int i = 0 , j = (m + n + 1 ) / 2 ; while (true ) { if (a[i] <= b[j + 1 ] && b[j] <= a[i + 1 ]) { int max1 = max (a[i], b[j]); int min2 = min (a[i + 1 ], b[j + 1 ]); return (m + n) % 2 ? max1 : (max1 + min2) / 2.0 ; } i++; j--; } } };
2️⃣ 用二分查找优化: 由于满足点只有一个, 所以判断条件为 $a[i] <= b[j + 1]$ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public : double findMedianSortedArrays (vector<int >& a, vector<int >& b) if (a.size () > b.size ()) swap (a, b); int m = a.size (), n = b.size (); a.insert (a.begin (), INT_MIN); b.insert (b.begin (), INT_MIN); a.push_back (INT_MAX); b.push_back (INT_MAX); int left = 0 , right = m + 1 ; while (left + 1 < right) { int i = (left + right) / 2 ; int j = (m + n + 1 ) / 2 - i; if (a[i] <= b[j + 1 ]) { left = i; } else { right = i; } } int i = left; int j = (m + n + 1 ) / 2 - i; int max1 = max (a[i], b[j]); int min2 = min (a[i + 1 ], b[j + 1 ]); return (m + n) % 2 ? max1 : (max1 + min2) / 2.0 ; } };
230. 二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素
腾讯 WXG 一面
✅ LeetCode:230. 二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 k ,请你设计一个算法查找其中第 k 小的元素(从 1 开始计数)。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1 输出:1
1️⃣ 中序遍历:在中序遍历,即「左-根-右」的过程中,每次递归完左子树,就把 k 减少 1,表示我们按照中序遍历访问到了一个节点。如果减一后 k 变成 0,那么答案就是当前节点的值,用一个外部变量 ans 记录。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public : int kthSmallest (TreeNode* root, int k) int ans; auto dfs = [&](this auto && dfs, TreeNode* node) -> void { if (node == nullptr ) { return ; } dfs (node->left); if (--k == 0 ) { ans = node->val; } dfs (node->right); }; dfs (root); return ans; } };
2️⃣ 中序遍历:直接将所有答案记录到 vector 数组中,返回对应索引值即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public : vector<int > ans; void preOrder (TreeNode* node) if (node == nullptr ) return ; preOrder (node->left); ans.push_back (node->val); preOrder (node->right); } int kthSmallest (TreeNode* root, int k) preOrder (root); return ans[k - 1 ]; } };
354. 俄罗斯套娃信封问题
腾讯 WXG 一面
✅ LeetCode:354. 俄罗斯套娃信封问题
给你一个二维整数数组 envelopes ,其中 envelopes[i] = [wi, hi] ,表示第 i 个信封的宽度和高度。
当另一个信封的宽度和高度都比这个信封大的时候,这个信封就可以放进另一个信封里,如同俄罗斯套娃一样。
请计算 最多能有多少个 信封能组成一组“俄罗斯套娃”信封(即可以把一个信封放到另一个信封里面)。
注意 :不允许旋转信封。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:envelopes = [[5,4],[6,4],[6,7],[2,3]] 输出:3 解释:最多信封的个数为 3, 组合为: [2,3] => [5,4] => [6,7]。
示例 2:
1 2 输入:envelopes = [[1,1],[1,1],[1,1]] 输出:1
0️⃣ DP 会超时,只能用二分查找。
1️⃣ 贪心 + 二分查找:先排序,再按照 LIS 二分贪心模板求最长递增子序列。因为二者都必须是递增的,所以第二维度需要逆序排序 ,使得第一维度相同的多个数,最后一个插入的一定是最小值,这样能嵌套的信封最多。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public : int maxEnvelopes (vector<vector<int >>& envelopes) sort (envelopes.begin (), envelopes.end (), [](const auto & a, const auto & b) { return a[0 ] < b[0 ] || (a[0 ] == b[0 ] && a[1 ] > b[1 ]); }); vector<int > g; for (auto & e : envelopes) { auto it = lower_bound (g.begin (), g.end (), e[1 ]); if (it == g.end ()) { g.push_back (e[1 ]); } else { *it = e[1 ]; } } return g.size (); } };